🧐 Risk based testing
26/03/2023
Risk-Based Testing (RBT) - Testing based on risk assessment means managing, prioritizing and performing tests with the risk of their occurrence and impact on the operation of all or part of the system/application in mind. It also means that we are aware that the user may encounter a bug 🐛 in the application, but it will in no way prevent him from continuing to use it and will not have a negative impact on the business functionality of the application. It is recommended to adopt this application testing/coverage strategy when:
Significance criteria:
- testing an application where its individual parts are extremely high risk (then they gain high priority and require a lot of attention) e.g. banking applications, health management applications.
Time criteria:
- testing can become a kind of bottleneck when releasing new versions of the application (regression takes a long time), which occur regularly and their deadlines are set in advance.
- when there are delays in creating the entire application (e.g. by adopting a waterfall strategy for creating the product)
- when the application is tested for the first time
Implementation:
- Risk identification (likelihood vs. business significance/keyness for business) - based on adopted risk criteria.
- Prioritization of modules, parts of the application (tests).
- Planning the tests to be performed
What benefits come from adopting this testing strategy?
- Focusing attention on tests that take the end user into account [what the user wants/needs from the business perspective of the product being created]
- Meeting the time criterion related to completing the task.
- Optimization of QA work/attention in a specific direction.
Risk:
- Lack of understanding of the most important parts from the business point of view of the product being developed.
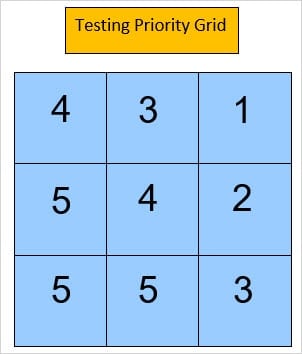
Risk Analysis Methodology - 2x2 matrix (3x3 High/Medium/Low possible)
High +----------++----------+
| Could | Must |
Risk | Test | Test |
| | |
Pro +----------++----------+
ba +----------++----------+
bili | Could | Should |
ty | Test | Test |
| | |
Low +----------++----------+
Low Risk Impact HighThere is no single key within which it is possible to determine the risk for each application. This can be based on both individual functionalities and usage paths, requirements, planned tests.
Likely/Quite Likely/Unlikely Minor/Visible/Interruption
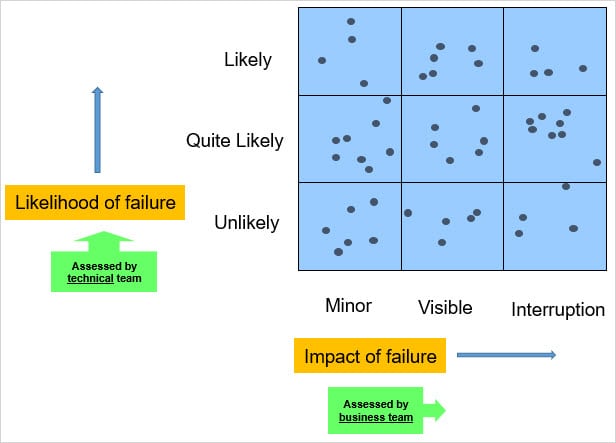

- Risk Assessment *
- Collecting assessments and mapping them on the matrix
- Determining testing priorities based on the matrix
- Defining the scope of testing individual parts of the application
Risk probability should be assessed by people with technical competencies in the team. Introducing markings during production e.g. Severity 1-4 / Priority 1-4 / Criticality 1-4
Sources:
Introducing change: Risk based regression
Risk Based Testing: Approach, Matrix, Process & Examples
The Ultimate Guide To Risk Based Testing: Risk Management In Software Testing
When Should You Take a Risk-based Approach to Testing and How To Implement It Right?